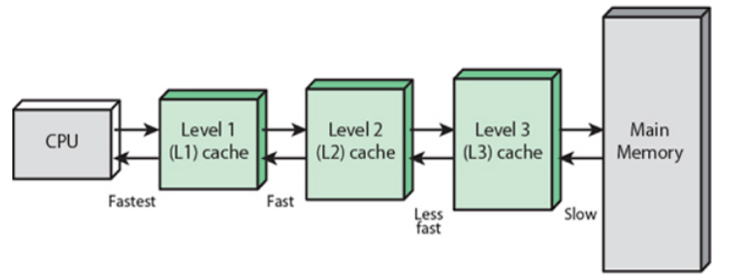
Describe the Three Levels of Cache Used by a Processor.
The reason it comes in such small amounts is the manufacturing cost and density. A Cache Pronounced as cash is a small and very fast temporary storage memory.

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times
There are three general cache levels.

. There is three types of cache. Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. It separates the computer storage based on hierarchy.
L1 cache is die L2 cache is off the die L3 cache is shared What can a DIMM use to hold data and amplify a signal just before the data is written to the module. It stores data that is not stored in L1 and L2 cache. Describe the three levels of cache used by a processor.
L1 L2 and L3. Memory within the processor housing but not on the processor die 3. Optical disks or magnetic types or tertiary Memory.
Generally the L1 cache is the smallest in size and built into the processor chip. L1 is usually part of the CPU chip itself and is both the smallest and the fastest to access. Part of the processor chip Primary Cache L1 2.
Another aspect to the complexity of cache revolves around how data is kept across the various levels. CPU Cache memory is divided into three levels. So does the CPU cache size make a difference to performance.
Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. L1 is the fastest and has the least amount of storage while L2 and L3 become slower but have higher storing capacity. Cache is graded as Level 1 L1 Level 2 L2 and Level 3 L3.
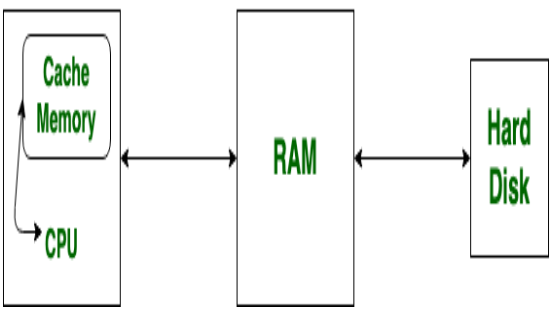
It is faster than RAM and the datainstructions that are most recently or most frequently used by CPU are stored in cache. Direct Mapping The simplest technique known as direct mapping maps each block of main memory into only one possible cache line. L2 cache or secondary cache is often more capacious than L1.
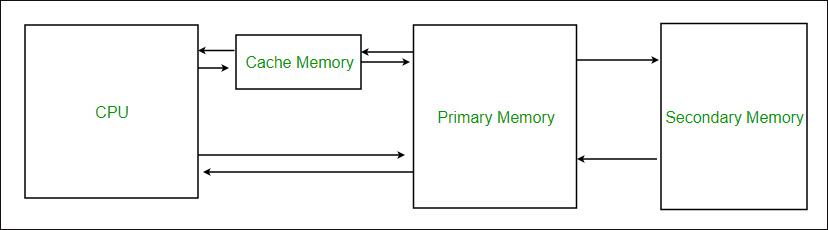
The term cache hit means the data or instruction processor need is in cache cache miss in the opposite situation. It is located inside or close to the CPU chip. There can be various levels of cache memory they are as follows.
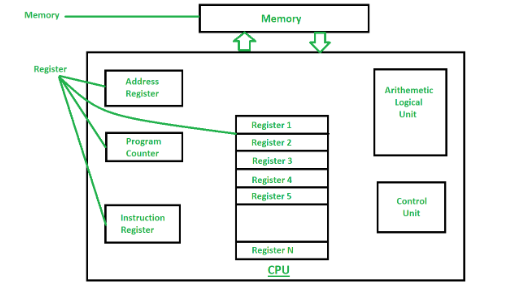
There are multiple different kinds of cache memory levels as follows Level 1 L1 or Registers It is a type of memory in which data is stored and accepted that are immediately stored in the CPU. Cache memory within a computer is classified under various types depending upon its physical location within the computer whether they are. Memory on the processor chip is called level 1 cache.
Also all the cores in the CPU share the same L3 cache memory. These are explained below. In a fully associative cache every memory location can be cached in any cache line.
Level 2 L2 or Cache Memory. Moreover L3 cache is the largest among all caches. Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache.
L1 Level 1 cache is the fastest memory that is present in a computer system. 1 2 3. Located between the processor and main memory Secondary Cache L2 3.
Among other things this makes accessing them slower and consume more energy for various reasons. Examples of L1 cache are. A second point is that L1 caches deal with different types of accesses than other levels in the cache hierarchy.
Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache. The Levels of CPU Cache Memory. L1 cache or primary cache is extremely fast but relatively small and is usually embedded in the processor chip as CPU cache.
There are three different types of mapping used for the purpose of cache memory which are as follows. A Level 3 L3 cache is a specialized cache that that is used by the CPU and is usually built onto the motherboard and in certain special processors within the CPU module itself. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache.
Memory further from the processor core then L2 cache but still within the processor housing. In Memory Hierarchy the cost of memory capacity is inversely proportional to speed. Parity A DDR4 DIMM running at a speed of 2666 MHz has what PC rating.
In other words if the CPU cannot find the data it is looking for in L1 and L2 cache it checks L3 cache. It is designed to speed up the transfer of data and instructions. L1L2 inclusive cache L3 victim cache write-back polices even ECC.
In multi-core CPUs a separate L1 cache is available for each core. What is L3 Cache. The memory hierarchy is again according to the speed and thus the size of the cache.
External to the processor Main Memory L3. Level 3 L3 Cache. Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2.
Main memory or primary memory. For example instruction register program counter accumulator address register etc. Describe the three levels of cache used by a processor.
L1 caches are sized so theyre large enough to be useful but small enough so theyre still fast to access. Every modern processor comes with a dedicated cache that holds processor instructions and data meant for almost immediate use. Memory on the processor die 2.
Earlier L2 cache designs placed them on the motherboard which made them quite slow. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. Direct mapping Associative mapping and Set-Associative mapping.
Magnetic disks or secondary memory. It works together with the L1 and L2 cache to improve computer performance by preventing bottlenecks due to the fetch and execute cycle taking too long. Level 1 L1 or Registers It stores and accepts the data which is immediately stores in the CPU.
L3 cache is the level 3 cache. Its size is often restricted to between. This is referred to as the first level cache.
A level 2 cache L2 cache is a CPU cache memory that is located outside and separate from the microprocessor chip core although it is found on the same processor chip package. Cache currently comes in three levels L1 L2 and L3. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache.
L1 L2 and L3.

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times

What Is Intel S New Core I9 Cpu Series Intel Core Intel Computer Processors

Nokia Lcd Eith Rasberry Pi Embedded Systems Pinterest Rasberry Pi

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times
What Is The Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache Pediaa Com
Cache Memory And Its Different Levels
Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times
An Introduction To Cache Memory Definition Types Performance

Apple Imac 21 5 Inch 8gb Ram 256gb Ssd Imac Ssd Product Review Videos

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times

Dell Precision T7610 Dell Precision Networking Workstation
Difference Between Cache Memory And Register Geeksforgeeks

Difference Between L1 L2 And L3 Cache How Does Cpu Cache Work Hardware Times
Arm Cortex A Series Programmer S Guide For Armv8 A
What Limits The Levels Of Cache Why Are There Only Two Or Three Levels Of Cache Quora


Comments
Post a Comment